
Write something
Day 2 : Macronutrients Balance 🥭🥑🍗
What Are Macronutrients?🧬 Macronutrients are the three main nutrients your body needs in large amounts: Carbs, Protein & Fats They help 'build' the foundation for the body's basic functions and are a source of energy. In order to protect yourself and your body, it is important to maintain a balanced diet, taking into account the daily dose of nutrients. ✅ Proteins - They have been described as the body's main 'building material', but this is by no means their only function. Hormones and enzymes made from proteins regulate metabolic processes. The dermis is made up of collagen, keratin and elastin proteins. Skeletal muscles move the body, and smooth muscles of the internal organs are responsible for peristalsis and regulating the lumen of blood vessels. Immune cells fight bacteria and viruses, and blood components transport nutrients around the body. All these functions are carried out by protein structures. ✅ Carbohydrates - The main source of energy. Complex carbohydrates (polysaccharides) are broken down by enzymes and converted into glucose. The oxidation of glucose provides energy for all life processes. Polysaccharides create an energy reserve in the body - in humans called glycogen. Complex carbohydrates, which are not digested, help the gut to function properly and 'feed' the beneficial microflora in it - these are fibre. ✅ Fats - They are necessary for the production of hormones, the assimilation of fat-soluble vitamins, the maintenance of elasticity of vessel walls and intercellular membranes.Fats form a cushion of fat between internal organs, protecting them from shock and displacement. The balance of Proteins , Carbs and Fats can be calculated in grams per kilogram of body weight or as a percentage of the required calories in the daily diet. 📊Daily norms of macronutrients per 1 kg of weight:📊 1.5-2 g protein 0.8-1.5 g of fat And carbs should be calculated according to energy consumption Me: weight 59 kg 118 g of protein (took 2 g because I train alot)
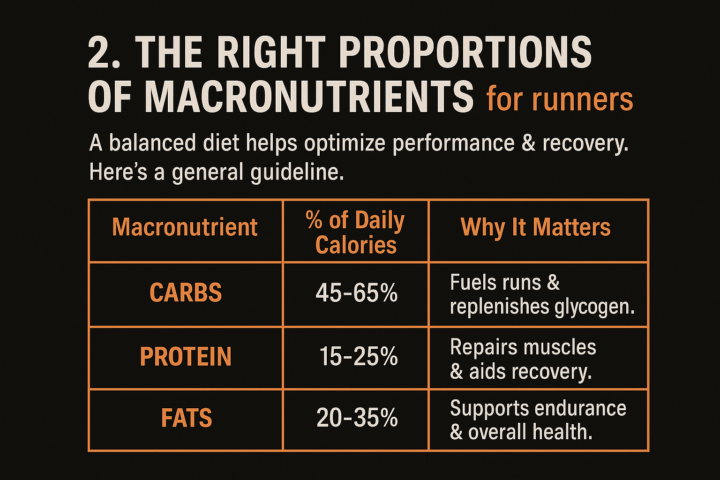
Day 4 : Сarbohydrates
Carbs often get a bad rap, but for active individuals like us, they’re a key fuel source! Let’s break down the truth about carbohydrates—how to use them wisely, why they matter, and how to avoid common pitfalls. The truth is that it's the amount of carbohydrates we eat that regulates our hunger. Not satiety, but hunger. Our bodies are smart and give us the right signals. So if we feel hungry, have headaches, are foggy, cranky, cold and think about food all the time, there is a good chance that we have too few carbohydrates in our diet. This is a common mistake made by those who plan their diets to achieve a calorie deficit. Sometimes that happens just because we underestimate our energy needs (common within people going to the gym or doing endurance sports) 😱 But What If I’m Gaining Weight? Let’s bust a myth: Carbs don’t make you fat. Overeating anything chronically does—but in endurance sports, under-fueling is far more common and dangerous than over-fueling. ⛔Don’t Fear Carbs!⛔ Carbs = primary fuel for endurance and high-intensity training. Also for muscle building foundation (they help protein synthesis) Cutting them too low can lead to: - Low energy & poor recovery - Increased hunger (thanks to hormone imbalances) - Slower metabolism over time (a lot of people are already in that trap ) Signs Your Carb Intake Is Too Low 🚩 Constant fatigue, poor workout performance 🚩 Insatiable hunger & cravings (especially for sugar) 🚩 Mood swings, poor sleep, feeling cold often In fact, many people lose weight more easily when they include carbs smartly, because: - You have better energy to move and train - Your hormones stay in balance - You avoid binge-eating from restriction 🔥 How Many Carbs Do Runners Need? Your carb intake should scale with training volume and intensity. Here’s how to calculate it: General Guidelines (per day) - Sedentary/Low Activity: 2–3g per kg of body weight - Moderate Exercise (30–60 min/day): 4–5g per kg - Endurance Training (1–2 hrs/day): 5–7g per kg - High-Volume/Intense (2+ hrs/day or racing): 7–10g per kg

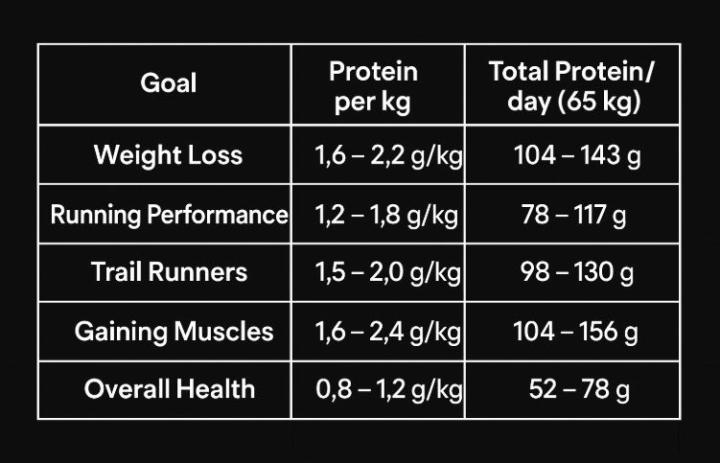
Day 3 - Deep Dive : Protein 🦐
Proteins are essential macromolecules made up of amino acids, often referred to as the "building blocks of life." Protein isn’t just for bodybuilders—it’s essential for every cell in your body. Ignoring protein needs can lead to serious health declines, while optimizing intake improves strength, immunity, and beauty. 🧾Even its name hints at this. The Greek word proteos means ‘primary’ or ‘first place’. Practice and statistics show that most people consume far less protein than they need. The restaurant industry offers us portions that consist mostly from carbohydrates and fat (cheaper, tastier). Evolutionarily, humans want to consume carbohydrates and fat to feel full quickly, so relying on sensation is not an option. That is why we have to create our own understanding of a balanced plate. I believe that controlling and consuming enough protein solves half the problems related to health, weight and athletic performance. We grossly underestimate the importance of protein in diets. So here is a detailed breakdown of the importance of protein.👇 🔍 Symptoms of Protein Deficiency ✔ Muscle Weakness & Loss (Sarcopenia) – Body breaks down muscle for energy. ✔ Fatigue & Low Energy – Lack of amino acids affects ATP (energy) production. ✔ Slow Recovery from Injuries – Wounds heal poorly due to insufficient tissue repair. ✔ Frequent Hunger & Cravings – Protein helps regulate appetite; deficiency leads to overeating carbs/fats. ✔ Frequent Infections – Low antibodies (immunoglobulins) weaken defense against viruses/bacteria. ✔ Mood Swings & Brain Fog – Neurotransmitters (like serotonin & dopamine) rely on amino acids. ✔ Irregular Blood Sugar – Protein stabilizes glucose; deficiency can mimic prediabetes symptoms. ✔ Dry, Flaky Skin – Reduced collagen leads to premature wrinkles. ✔ Brittle Nails – Nails become soft, peel, or develop ridges. ✔ Micronutrient Gaps: Low-protein diets often lack zinc, selenium, and vitamins C/D/E 💡 Who is at Higher Risk? - Elderly (reduced appetite, muscle loss) - Vegans/Vegetarians (if not balancing plant proteins properly) - People with Eating Disorders (anorexia, bulimia) - Athletes Overtraining Without Proper Nutrition ❗
Day 1 - Calories - Your Body’s Energy Engine 🚀
I know calories can make you anxious. You will say: it's complicated, boring, old-fashioned or even dangerous for mental health. There are fancy types of diets: interval fasting, intuitive, paleo, keto plant-based and so on - everything but not the principles of the scientific approach to food. The truth is that calories were invented as a tool, a measure of energy. I believe that basic understanding of how our metabolism works can help us achieve our goals more efficiently. That is why I want to teach you to understand how our energy metabolism works and to decide for yourself how much energy we need to use to achieve certain goals. 🟢Goal: understand your baseline calorie needs (BMR), active calorie expenditure, and how to calculate total daily energy expenditure (TDEE). 🟣Purpose: The foundation for setting calorie goals (weight loss/maintenance/gain). Maintaining energy balance, avoiding red-s (relative energy syndrome in sports), eliminate vitamin and mineral deficiencies. 👉Basal Metabolic Rate (BMR)👈 So our bodies need energy mainly to keep us alive - breathing, blood circulation, body temperature, organ function and so on. The energy required for these processes is called basal metabolic rate. Our basal metabolic rate can be calculated using this formula: Mifflin-St Jeor Equation : - Men: BMR = (10 × weight in kg) + (6.25 × height in cm) – (5 × age) + 5 - Women: BMR = (10 × weight in kg) + (6.25 × height in cm) – (5 × age) – 161 My baseline metabolism : (10x59) + (6.25 x 168) - (5 x 31) - 161 = 1324 cal 🛌We have calculated the amount of energy our body needs even if we lie in bed all day.🛌 It is important to realise that we should never approach such low levels of energy intake when we are moving, walking, talking, exercising, as this would mean a severe energy deficit. However, when trying different diets to lose weight, people often limit themselves to consuming even less energy than they need to maintain their metabolism. ⛔
Food = Fuel = 50% of Result
Time to think about next challenge! 🏋️♀️ I have an idea - one of the most important aspects of running performance is nutrition. 🥑 And I think that organising meals, helping each other with advice and monitoring our plates can make a huge difference. I have a lot of knowledge about how people involved in fitness activity, especially running, should eat. What we can speak about? ✅Hydration ✅Breakfast balance ✅Pre-run Fuel ✅Protein Intake ✅Post training recovery meals ✅Healthy fats balance ✅Calorie intake ✅Macro nutrients : Carbs/ Fats / Proteins 🥞🍓🥩 We can also share our recipes and plates - which is sure to help you adapt your meals and learn something new. What are your thoughts? What challenges do you face with your diet?

1-17 of 17

skool.com/become-better-runner-4238
Welcome to Better Runner ! This is where runners of all levels achieve their goals.
Powered by





