Activity
Mon
Wed
Fri
Sun
Mar
Apr
May
Jun
Jul
Aug
Sep
Oct
Nov
Dec
Jan
Feb
What is this?
Less
More
Owned by Dr. Spyros
A beginner-friendly training program for a career in the energy sector. Regardless of your location, age, sex, education or experience level.
Memberships
169 contributions to Energy Economics & Finance
Interview Questions (Since October 2025)
The goal of this community is to help you secure jobs across the wider energy sector. That includes: - Major Energy Firms (Trading houses, Utilities, Oil & Gas). - Non-Energy Firms that manage their own energy assets or investments. - Academia (PhD applications and research roles). I have compiled a list of recent questions that candidates have faced in interview stages mostly between October 2025 and January 2026 ( retrieved from student databases ). You can also see below the company they were applying to. When reading these questions we need to ask ourselves: "Could I answer this question under pressure (with maybe 1 minute of thinking)"? Also, my answers to each question are in Classroom 6.3 compiled in the form of a PDF file. This PDF file has 5 more questions included as well (and answers). 1. Energy Quant (Power/Gas) - BP: “Walk me through a forward-curve model you would use for power or gas. How do you handle seasonality, mean reversion, and spikes?” - Shell Energy Trading: “Design a risk framework for an options book on power. Which metrics would you report daily, and how would you stress test extreme events?” 2. Energy Trader - TotalEnergies: “Explain the spark spread and how it links fuel prices, heat rate, and power prices. When does a plant dispatch?” - Trafigura: “You have a short physical position for next month. How would you hedge it with futures, swaps, and optionality, and what basis risks remain?” 3. Electricity Market Analyst (ISO/Utility) - National Grid ESO: “Explain Locational Marginal Pricing (LMP): what are its components, and what data does the market-clearing optimization need?” - EPRI: “How would you build a day-ahead load forecast and quantify uncertainty? Which error metrics matter most for operations?” 4. Project Finance Analyst - Macquarie: “Define DSCR and explain how it drives debt sizing. What DSCR range would you expect for a contracted wind or solar project?”
Research paper: Machine Learning for Solar Energy Economy
Few professionals in energy also read research publications. There are over 200 such analysis in sections 6.1 and 6.4 in the Classroom. Below is a popular paper connecting solar PV economics, machine learning and energy storage. Below there is also a brief summary. Scroll down to download it. - Title: Optimizing distributed solar energy economics: A machine learning classification approach to storage system management - Citation: Wenhui, L., Li, H., Laghari, M. A., Guliyeva, S., Amonova, N., & Yuan, H. (2025). Optimizing distributed solar energy economics: A machine learning classification approach to storage system management. Case Studies in Thermal Engineering, 75, 107106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.csite.2025.107106 - Downloadable resource is attached below Key Points: Solar energy is a clean resource, but it faces a major challenge because the sun does not shine consistently. This makes it difficult to match the amount of electricity generated with the amount people need to use. Batteries are used to store extra energy for later, but they are expensive and can wear out if used incorrectly. Traditional methods for managing this storage often fail to look at both the technical needs and the financial costs at the same time. The researchers in this study developed a new method to solve these problems using a type of artificial intelligence called K-Nearest Neighbors or KNN. This is a classification tool that looks at past examples to decide what to do in the current situation. Instead of only focusing on the technical side of things, this new system includes economic factors. It helps the system decide the best times to charge or discharge the battery to save the most money. The study uses a concept called entransy dissipation theory alongside the computer model. This is a physics principle that measures the loss of energy quality during transfer processes. By using this theory, the system ensures that energy is not just stored, but is kept at a high quality. This approach balances the need to save energy quantity with the need to maintain its usefulness, which helps in reducing the overall costs of running the system.
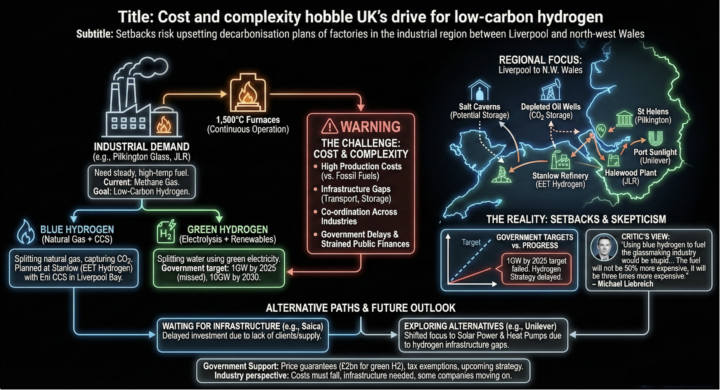
An illustration about Hydrogen
Here is a plot about hydrogen in the United Kingdom. The plot shows that energy factories need steady, very high temperature heat, around 1500°C, running continuously, and today they mainly burn methane gas. Their plan is to switch to low carbon hydrogen, either ‘blue hydrogen’ made from natural gas with carbon capture and storage or ‘green hydrogen’ made by splitting water using renewable electricity. But the central barrier is cost and complexity: hydrogen is still expensive to produce, transport and store, and it requires coordinated investment across multiple industries and public infrastructure.
New Report on Hydrogen
A new report on energy trends has been published and can be found by clicking on ‘Classroom’ and navigating to Section 6.2 (see the attached screenshot). You can use this report and the visualisations it includes, in your own projects, work, or studies, without limits. This report explains the progress for the UK’s hydrogen rollout. The report includes diagrams and flowcharts that provide context, and also a list of relevant sources that were used to complete this report. These sources are from the Financial Times, Wall Street Journal, the Economist and Investors Chronicle (all sources are available inside the report). Your subscription in this Skool community gives you access to paywalled energy-economics articles from these publications (Financial Times etc) indirectly through these reports. I have also included some explanations and additional text that explains some details. The text is written in beginner-friendly, easy-to-understand language. Reading these reports can help with interviews, meetings, presentations, networking, and public speaking. Strongly recommended.
New Report on Small Nuclear Reactors
A new report on energy trends has been published and can be found by clicking on 'Classroom' and navigating to Section 6.2 (See the attached screenshot). You can use this report and the visualisations it includes, in your own projects, work, or studies, without limits. This report is about Small Nuclear Reactors and current trends by February 2026. Big technology companies like Amazon and Google are racing to find reliable electricity to meet the massive energy demands of new AI data centers. Their primary long-term solution is investing in Small Modular Reactors (SMRs) which are smaller nuclear plants that provide steady "zero-emission" electricity. However, because SMRs take about 8 years to build, these companies are also restarting and upgrading existing nuclear plants to bridge the gap. The report includes lots of diagrams and flowcharts that provide context, and also a list of relevant sources that were used to complete this report. These sources are from the Financial Times, Wall Street Journal, the Economist and Investors Chronicle (all sources are available inside the report). Your subscription in this Skool community gives you access to paywalled energy-economics articles from these publications (Financial Times etc) indirectly through these reports. I have also included some explanations and additional text that explains some details. The text is written in beginner-friendly, easy-to-understand language. Reading these reports is helpful for interviews, panel discussions , presentations, networking, and public speaking. Strongly recommended.
1-10 of 169
@sp-ia-8683
PhD in Energy, Imperial College London | Author of over 40 publications | 1100+ citations | Energy Consultant in $50m+ energy projects
Active 16m ago
Joined Aug 20, 2024
London, U.K.

