Activity
Mon
Wed
Fri
Sun
Mar
Apr
May
Jun
Jul
Aug
Sep
Oct
Nov
Dec
Jan
Feb
What is this?
Less
More
Memberships
0wnable.io
1.3k members • $99/m
17 contributions to 0wnable.io
What is a BlockChain? 🧱⛓️💥
A blockchain is a digital record - but not just any record. It’s a way of storing information that’s shared across thousands of computers, all over the world, with no single person or company in charge. Everyone sees the same version. No one can quietly change the past. Once something is added, it stays there. Forever. This might sound simple, but it’s a major shift in how we store and agree on information. Most digital systems today rely on a central authority - a bank, a company, a platform. If you send money, a bank updates its private records. If you post online, a platform decides what’s shown and what disappears. With a blockchain, the record belongs to the network. Anyone can verify it - no one can secretly rewrite it. That’s the breakthrough. Instead of trusting one central source, blockchains rely on thousands of independent computers working together. Every transaction is checked, confirmed, and locked into place by the network. The rules are written in code. No backdoors, no special treatment. That’s what people mean by trustless - not that there’s no trust, but that it’s built into the structure. Here’s how it works: When someone sends coins, interacts with an app, or stores data, that action is shared with the network. These actions are grouped into a block (like a page in a public ledger) and checked against the rules. Once confirmed, the block is added to the chain - linked to the one before it, forming a permanent, tamper-proof history. Every node keeps a copy. If anyone tries to cheat, the network rejects it. Simple, secure, unstoppable. Blockchains started with payments (Bitcoin), but quickly evolved. Ethereum introduced smart contracts — programmable rules that live on-chain. Now we’ve got decentralised finance, player-owned games, tokenised art, and communities that run themselves. All of it running on open infrastructure, visible to anyone, controlled by no one. So why now? Because the internet is centralised, fragile, and full of middlemen. Platforms gatekeep. Payment processors block. Governments shut things down. Blockchains offer a new foundation: transparent, permissionless, and built to last. They’re not faster or cheaper than today’s systems - but they’re more fair, resilient, and open by default.
3
0

More Than Magic Internet Money: A Beginner’s Guide to Crypto
So, what even is Crypto? Let’s strip it right back. You hear it everywhere — crypto, Bitcoin, blockchain, web3, decentralisation, NFTs, staking, L1s, L2s, DeFi, DeSci, De-just-about-everything — but what is it? And why does it matter? More importantly, is it actually worth paying attention to, or is this another overhyped internet fad destined to end up next to Beanie Babies and MySpace in the cultural dustbin? Short answer: crypto is not just internet money. It’s a new financial and computational fabric. And while it might wear the skin of speculative tech bros and Twitter memes, what’s underneath is a full-blown rearchitecting of how humans organise value, trust, and power on the internet. Longer answer? Keep reading. The Digital Ledger That Doesn’t Lie: At the heart of crypto is a very simple idea: a blockchain — a public, distributed record of transactions, validated by a decentralised network. That might sound boring. And it kind of is. But it’s also radical. Before crypto, you needed institutions - banks, governments, platforms - to act as arbiters of truth. They kept the records, enforced the rules, and usually took a cut while doing so. Crypto flips that model. It lets networks of strangers reach consensus without trusting each other - or a central referee. That means money, identity, agreements and ownership can all be coded directly into software — and verified by anyone. It’s programmable trust, built into open networks. No gatekeepers required. Ok, But… Why Does Any of This Matter? Here’s the thing: crypto isn’t just new tech. It’s a new social contract. In a world where institutions are increasingly centralised, opaque and fragile — crypto offers an alternative: a transparent, permissionless, globally accessible system. You don’t need a bank account. You don’t need to trust a CEO. You don’t need to be born in the right country. And while some of it is still chaos — with rug pulls, volatility and meme coins in the mix — the underlying trend is undeniable: crypto gives people more direct ownership of the digital world they interact with. And that shift - from centralised control to user sovereignty - is just getting started.
5
0

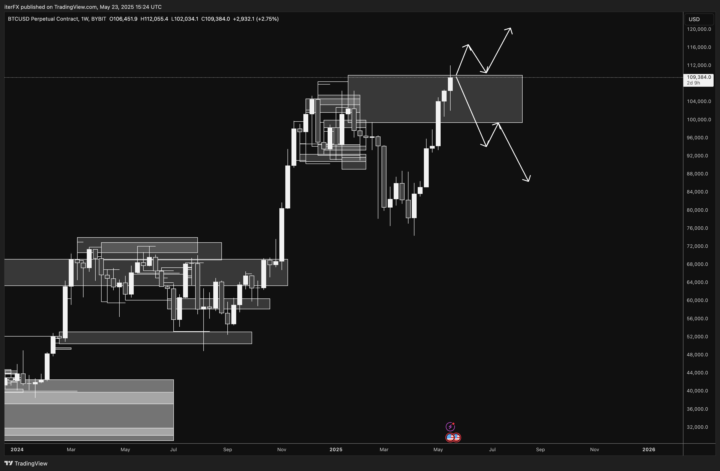
BTC: Where to next?!
Now that the dust has settled on BTC's new ATH of $112,055 we can shift our attention to the all important question: where do we go from here? As with all markets, the options are limited and as such seem simple, we can either go UP from here or we can go DOWN - seems easy, right? The reality is far from it, the market is designed to play with your emotions and pull on your heart strings before it reveals its true intentions. Below I have mapped out two potential scenarios based on the teachings from our syllabus. Which, if any, do you think is more likely to play out?
SYLLABUS Q&A: SYLLABUS GIVEAWAY 🙋🏽♂️ 🙋🏽♀️
Have you watched the first episode of our syllabus? If not head over to the ‘CLASSROOM’ tab and take a watch 💻 If you’ve already watched it and have any questions drop them below and a member of our team will get back to you with an answer! We will also select, at random, someone who’s asked a question to gain FREE ACCESS to our entire syllabus! 🎉 GET WATCHING AND GET ASKING 🚀👇🏽 (Remember to categorise your post into the ‘Syllabus Q&A’ section) https://www.skool.com/0wnableio-9008/classroom/43772348?md=d7aeb8319cbf48e0bbcc66dd1f2a3997
Gold Prices Up? 🥇
We know, gold isn’t crypto, but in today’s interconnected world, it’s important to understand how all markets influence each other. Traditional assets like gold still play a big role in shaping investor behaviour, and what happens in those markets often affects sentiment in the crypto space too. 📊 With tensions rising again in the Middle East, global markets are starting to feel the strain. Whether it’s escalating conflict, political instability, or the threat of oil supply disruptions, uncertainty like this always sends ripples through both traditional and digital finance. When things get shaky on the world stage, one thing remains consistent: investors look for safety. And that’s where gold comes in. 🪙 Gold has long been viewed as a “safe haven” asset. When fear rises and trust in markets dips, people move into gold to protect their wealth. Unsurprisingly, we’re already seeing gold prices climb as investors prepare for what may come next. But it’s not just gold that’s reacting, crypto is as well. While Bitcoin and the wider crypto market have often been seen as speculative, there’s a growing trend of people viewing Bitcoin as “digital gold”. In recent times, we’ve seen Bitcoin rally during global uncertainty, with more investors seeing it as a store of value that sits outside traditional systems. 📈 That said, crypto markets are still volatile, and the impact of geopolitical tension can go both ways. Short-term panic can trigger sell-offs, but over the longer term, uncertainty often drives more people towards decentralised assets. So, what’s the takeaway? In times like this, traditional assets like gold tend to shine, while crypto is steadily maturing into a modern safe haven, particularly for a younger, more digitally native generation of investors. Whether you’re deep into DeFi or still stacking bullion, these global events are a reminder that in finance, perception is everything, and stability is king. ✍️ Keep an eye on the headlines, world events move markets faster than ever. And in a world where control is often in question, assets like gold and crypto are more relevant than ever.

1-10 of 17
Active 206d ago
Joined May 23, 2025
Powered by

